Happy Tuesday! The past few days I was in Lausanne, Switzerland at Hacksummit, a climate tech conference. I had a great time meeting my investment group Climate Insiders, catching up with clients, and scoping out up and coming startups. On that note, today we’re diving deeper into circular design case studies so you can check out some real examples of how circular design can be applied in different industries.
The Core Principles of Circular Design
Let’s revisit circular design before we dive into a few examples. If you haven’t already, check out last week’s Introduction to Circular Design.
The 3 core principles of designing for a circular economy are:
Eliminate waste and pollution
Circulate products and materials
Regenerate nature
Great, now that we’ve refreshed our memory, let’s get into our examples. ⏬
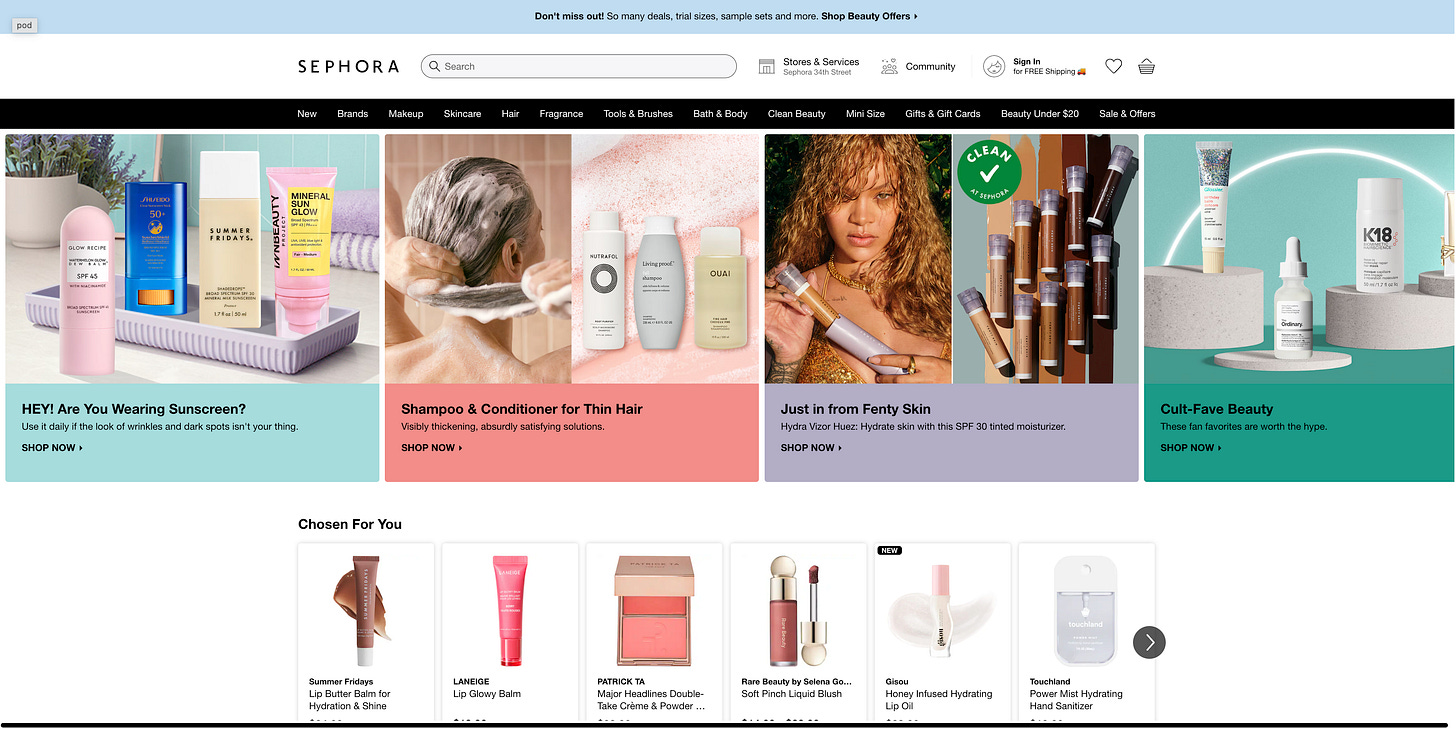
1. Recycling plastic waste in the beauty industry
Let’s talk about beauty. According to McKinsey, in 2022, the beauty market—defined as skincare, fragrance, makeup, and haircare—generated approximately $430 billion in revenue.1 Damn.🤑 Riri gets it.
Beauty is in an upward trend across all categories and even withstands the current turbulent macroeconomic environment. The beauty market is expected to reach approximately $580 billion by 2027 and with all this growth comes….can you guess? No, it’s not more beautiful people. 😂 It’s trash. More product means increased efforts to stand out via packaging leading to increased volumes of plastic waste. One of my recent investments actually tackles the challenge of textile and beauty waste in collaboration with L'Oréal. Very excited to see how it progresses.
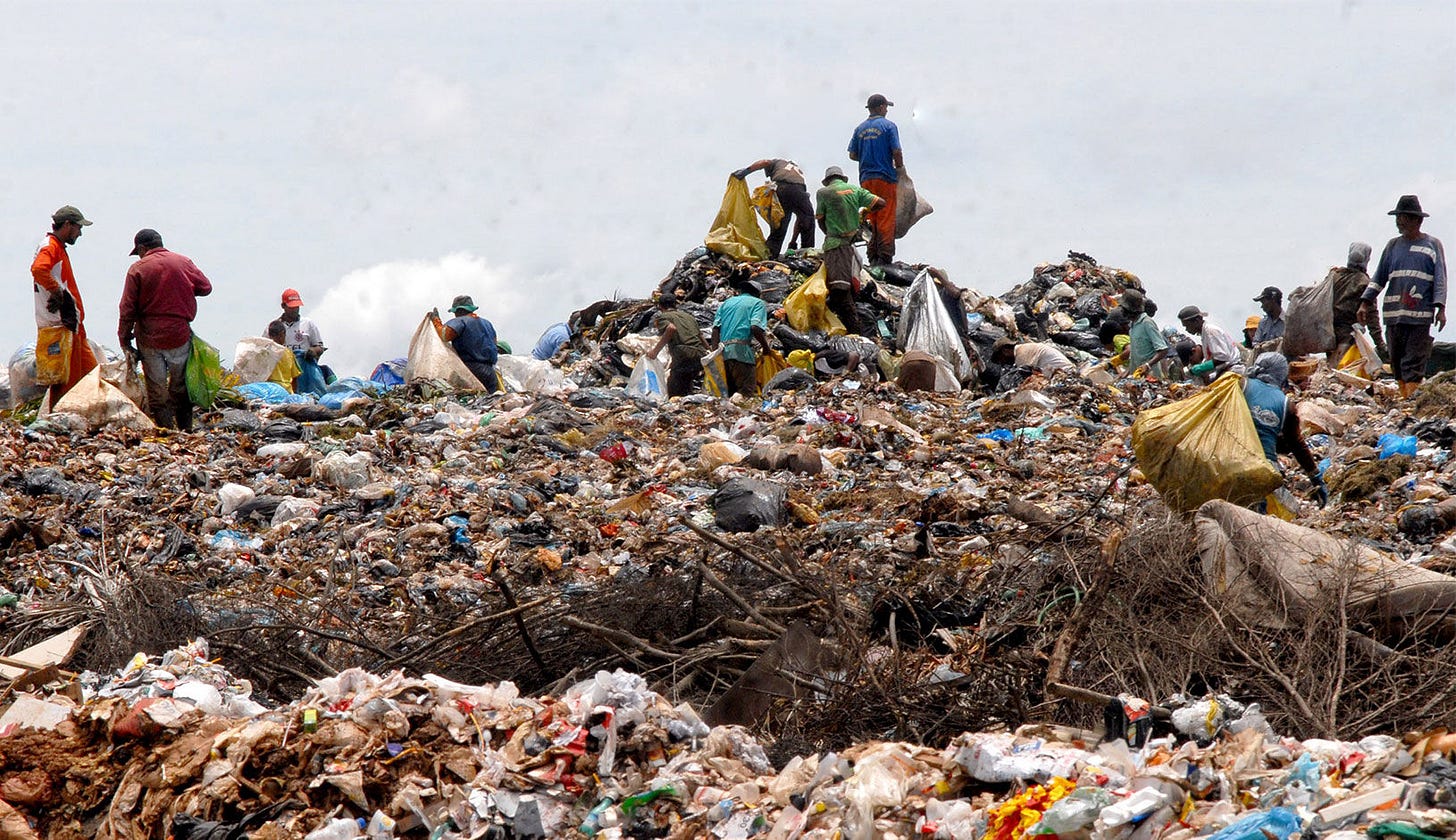
Okay, so none of us are surprised that plastic is a problem. 👀The thing is circular design can stop it from becoming waste. 🛑 In China, approximately 3 billion empty cosmetic bottles were produced in 2021, with 70% being incinerated or landfilled as general waste.2 Several makeup and personal care brands — such as L'Oréal, Procter & Gamble, Coty, L'Occitane, Shu Uemura, and Herborist — have initiated recycling schemes in China for empty packaging. The problem is waste is complex, hard to process, contains various materials, and is a challenge to capture from consumers.
Chinese company Yan An Tang (YAT) is tackling waste from cosmetics. How are they doing this? They’re leveraging technology. In 2021, YAT launched its platform, ‘Diary Recycle’, which is embedded in WeChat. 📲 In 2023, YAT ran a pilot with 448 Watsons stores — one of Asia’s biggest beauty retailers — to test in-store recycling models.
Key Challenges
Problem: YAT struggled to identify the brand of the empty bottles for sorting.
Solution: Image recognition technology. They accumulated 2 million data points to identify text information on empty bottles enabling the recyclers to differentiate between brands when there were no other visual markers.
Problem: Lack of standardization for sorting.
Solution: Users must adhere to recycling standards.
Problem: Lack of insights on packaging design and whether the composite material can meet recycling standards through technological processing.
Solution: YAT gathers data on material composition, weight, and other information about packaging, shares research, and encourages developmental conversations.
2. Leveraging e-waste to build digital equity in Brazil
E-waste is the fastest growing solid waste stream in the world; technology continues to advance at rapid rates, consumers are dumping their tech, and it often ends up in the global south. 🌍 A record 62 million tonnes (Mt) of e-waste was produced in 2022, Up 82% from 2010. According to the United Nations Institute for Training and Research, the world’s generation of electronic waste is rising 5x faster than documented e-waste recycling.3 😱 The dumping of e-waste also produces toxic chemicals leading to severe environmental consequences. Devices contain a variety of hazardous materials, including lead, mercury, and cadmium that end up permeating the ecosystem and posing a threat to not only the ecosystem, but also the wellbeing of local populations.
In the Brazilian city of Belo Horizonte, there was a large e-waste problem. The city solved this by creating computer reconditioning centers to restore these electronics. Instead of going to a landfill, they had a second life. They took unemployed youth from low-income communities to receive extensive training on how to restore the computers. The refurbished tech went to over 300 digital inclusion sites. This gave locals free access to technology and the internet. They also provided training to increase the digital literacy of the population. The beauty of this case study is that the circularity principles can also tackle social issues and have a positive impact on community building. 👏 The project has been a large success with 15,000 kg of post-use electronics diverted from landfill every year on average, since 2008.4
Key Challenges
Problem: Excessive waste from hardware being dumped in Belo Horizonte. (Brazil is the second largest producer of e-waste in the Americas.)
Solution: Restoration and refurbishing hardware for second life.
Problem: Excessive waste from hardware being dumped.
Solution: Restoration and refurbishing hardware for second life.
Problem: Low digital literacy in Belo Horizonte.
Solution: Access to free computers, internet, and digital literacy training.
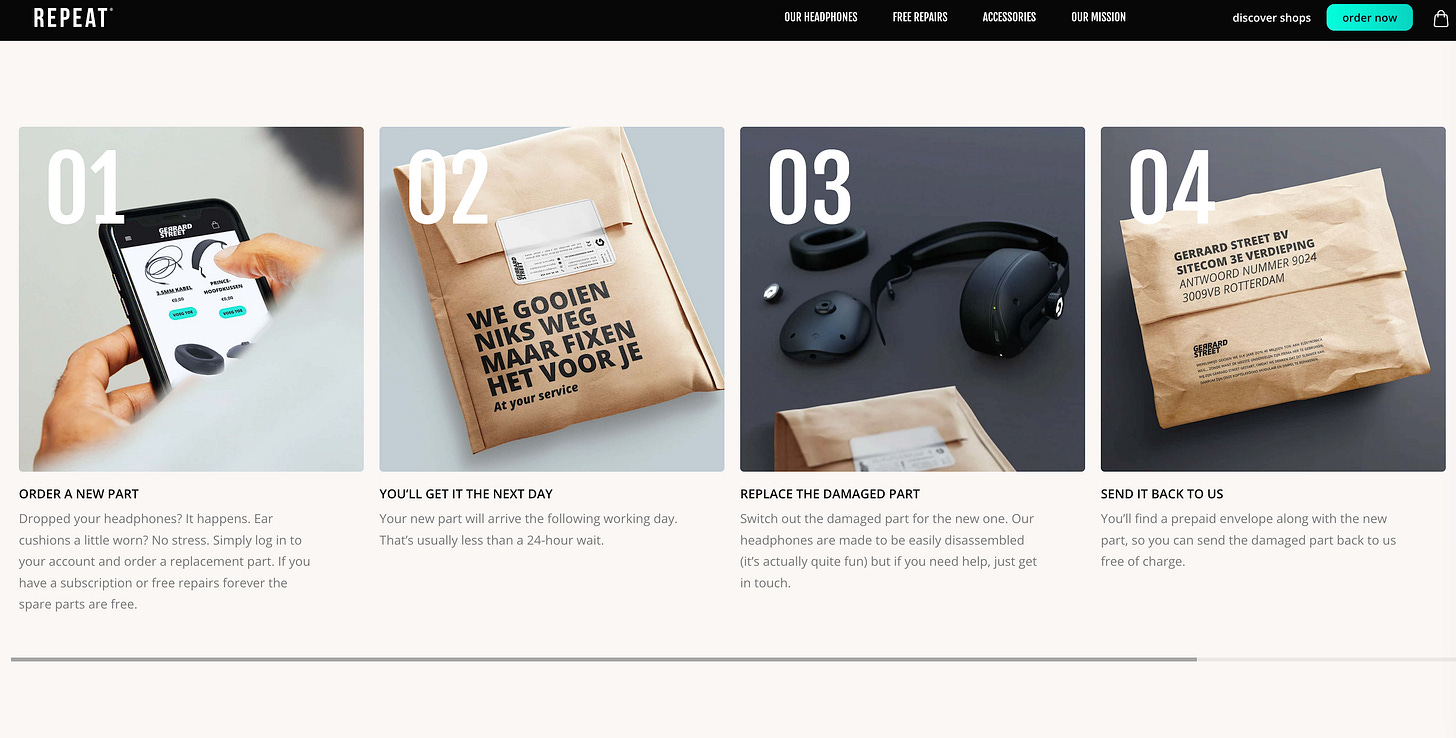
3. Modular headphone subscription to reduce waste
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to Conscious Tech to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.